-
Select Your Country
-
Afghanistan
-
Albania
-
Algeria
-
Andorra
-
Angola
-
Antigua and Barbuda
-
Argentina
-
Armenia
-
Australia
-
Austria
-
Azerbaijan
-
Bahamas
-
Bahrain
-
Bangladesh
-
Barbados
-
Belarus
-
Belgium
-
Belize
-
Benin
-
Bhutan
-
Bolivia
-
Bosnia and Herzegovina
-
Botswana
-
Brazil
-
Brunei
-
Bulgaria
-
Burkina Faso
-
Burundi
-
Côte d'Ivoire
-
Cabo Verde
-
Cambodia
-
Cameroon
-
Canada
-
Central African Republic
-
Chad
-
Chile
-
China
-
Colombia
-
Comoros
-
Congo (Congo-Brazzaville)
-
Costa Rica
-
Croatia
-
Cuba
-
Cyprus
-
Czechia (Czech Republic)
-
Democratic Republic of the Congo
-
Denmark
-
Djibouti
-
Dominica
-
Dominican RepublicRepublic
-
Ecuador
-
Egypt
-
El Salvador
-
Equatorial Guinea
-
Eritrea
-
Estonia
-
Eswatini
-
Ethiopia
-
Fiji
-
Finland
-
France
-
Gabon
-
Gambia
-
Georgia
-
Germany
-
Ghana
-
Greece
-
Grenada
-
Guatemala
-
Guinea
-
Guinea-Bissau
-
Guyana
-
Haiti
-
Hole See
-
Honduras
-
Hungary
-
Iceland
-
India
-
Indonesia
-
Iran
-
Iraq
-
Ireland
-
Israel
-
Italy
-
Jamaica
-
Japan
-
Jordan
-
Kazakhstan
-
Kenya
-
Kiribati
-
Kuwait
-
Kyrgyzstan
-
Laos
-
Latvia
-
Lebanon
-
Lesotho
-
Liberia
-
Libya
-
Liechtenstein
-
Lithuania
-
Luxembourg
-
Madagascar
-
Malawi
-
Malaysia
-
Maldives
-
Mali
-
Malta
-
Marshall Islands
-
Mauritania
-
Mauritius
-
Mexico
-
Micronesia
-
Moldova
-
Monaco
-
Mongolia
-
Montenegro
-
Morocco
-
Mozambique
-
Myanmar
-
Namibia
-
Nauru
-
Nepal
-
Netherlands
-
New Zealand
-
Nicaragua
-
Niger
-
Nigeria
-
Norway
-
Oman
-
Pakistan
-
Palau
-
Palestine
-
Panama
-
Papua New Guineaa
-
Paraguay
-
Peru
-
Philippines
-
Poland
-
Portugal
-
Qatar
-
Romania
-
Russia
-
Rwanda
-
Saint Kitts and Nevis
-
Saint Lucia
-
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
-
Samoa
-
San Marino
-
Sao Tome and Principe
-
Saudi Arabia
-
Senegal
-
Serbia
-
Seychelles
-
Sierra Leone
-
Singapore
-
Slovakia
-
Slovenia
-
Solomon Islands
-
Somalia
-
South Africa
-
South Korea
-
South Sudan
-
Spain
-
Sri Lanka
-
Sudan
-
Suriname
-
Sweden
-
Switzerland
-
Syria
-
Tajikistan
-
Tanzania
-
Thailand
-
Timor-Leste
-
Togo
-
Tonga
-
Trinidad and Tobago
-
Tunisia
-
Turkey
-
Turkmenistan
-
Tuvalu
-
Uganda
-
Ukraine
-
United Arab Emirates
-
United Kingdom
-
United States of America
-
Uruguay
-
Uzbekistan
-
Vanuatu
-
Venezuela
-
Vietnam
-
Yemen
-
Zambia
-
Zimbabwe
Welcome Educator
In this section you will find guidance on how to plan and teach wheelchair service content based on the World Health Organization 8 steps for manual wheelchair provision for users who can sit upright without postural support or with basic postural support needs.
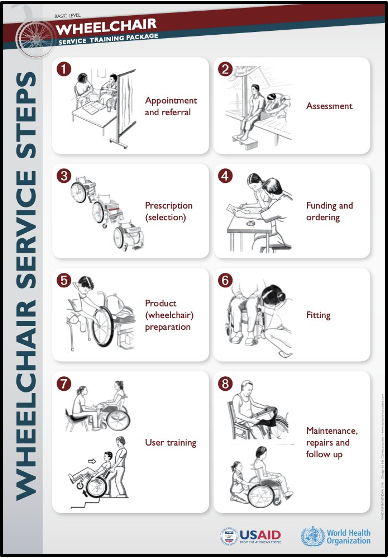
The scope of the content that you can teach will depend on your context such as the level of education of your program and the role of your profession in wheelchair services. This means that you may develop a dedicated wheelchair service course or that you may integrate the wheelchair service content within an existing course or clinical placement.
Let’s see a few examples on how what you teach is dictated by the context:
In context A, practicing OTs are responsible for assessing and prescribing wheelchairs. The educator can use the framework presented in the Introduction to the 8 steps; Step 2: Assessment and Step: 3 prescription to plan and develop
A new school of rehabilitation is starting a physiotherapy and a prosthetics and orthotics program. The school is interested in teaching these two professions to work together to establish a wheelchair service in the school. The educator will use the framework presented in the Introduction to the 8 steps for both programs and both will learn Step 6: Fitting; the physiotherapy will focus on Step 1: referral; Step 2: Assessment; Step: 3 prescription to plan and develop; and Step 7: User training while the P&O will focus on Step 4: Funding and Ordering; Step 5: Product preparation; Step 6: fitting and Step 8: Follow up.
A training centre is interested in integrating more wheelchair education in a continuing education course for spinal cord injury rehabilitation. The educator will use the framework presented in the Introduction to the 8 steps; and Step 7: User training
After you select the step you would like to teach, you will find general information about the content, and considerations for planning the course according to your context (e.g. human resources, infrastructure, equipment and tools, and documentation). The component also provides ideas to overcome potential challenges such as limited time, limited availability of wheelchair products, and lack of qualified trainers/providers.
You will also find learning objectives per service step, strategies of pedagogical delivery (how to teach the content), and student evaluation methods (how to evaluate the content), Links to resources that can be made use of in both the “How to teach the content” and “How to evaluate” have been provided in these sections. Some of these references are descriptions that educators can utilize in the design of their own material, and some of these resources are “ready-to-use” resources.
© ISWP – International Society of Wheelchair Professionals | The University of Pittsburgh – Department of Rehab Science
 Where are you?
Where are you?
-
Select Your Country
-
Afghanistan
-
Albania
-
Algeria
-
Andorra
-
Angola
-
Antigua and Barbuda
-
Argentina
-
Armenia
-
Australia
-
Austria
-
Azerbaijan
-
Bahamas
-
Bahrain
-
Bangladesh
-
Barbados
-
Belarus
-
Belgium
-
Belize
-
Benin
-
Bhutan
-
Bolivia
-
Bosnia and Herzegovina
-
Botswana
-
Brazil
-
Brunei
-
Bulgaria
-
Burkina Faso
-
Burundi
-
Côte d'Ivoire
-
Cabo Verde
-
Cambodia
-
Cameroon
-
Canada
-
Central African Republic
-
Chad
-
Chile
-
China
-
Colombia
-
Comoros
-
Congo (Congo-Brazzaville)
-
Costa Rica
-
Croatia
-
Cuba
-
Cyprus
-
Czechia (Czech Republic)
-
Democratic Republic of the Congo
-
Denmark
-
Djibouti
-
Dominica
-
Dominican RepublicRepublic
-
Ecuador
-
Egypt
-
El Salvador
-
Equatorial Guinea
-
Eritrea
-
Estonia
-
Eswatini
-
Ethiopia
-
Fiji
-
Finland
-
France
-
Gabon
-
Gambia
-
Georgia
-
Germany
-
Ghana
-
Greece
-
Grenada
-
Guatemala
-
Guinea
-
Guinea-Bissau
-
Guyana
-
Haiti
-
Hole See
-
Honduras
-
Hungary
-
Iceland
-
India
-
Indonesia
-
Iran
-
Iraq
-
Ireland
-
Israel
-
Italy
-
Jamaica
-
Japan
-
Jordan
-
Kazakhstan
-
Kenya
-
Kiribati
-
Kuwait
-
Kyrgyzstan
-
Laos
-
Latvia
-
Lebanon
-
Lesotho
-
Liberia
-
Libya
-
Liechtenstein
-
Lithuania
-
Luxembourg
-
Madagascar
-
Malawi
-
Malaysia
-
Maldives
-
Mali
-
Malta
-
Marshall Islands
-
Mauritania
-
Mauritius
-
Mexico
-
Micronesia
-
Moldova
-
Monaco
-
Mongolia
-
Montenegro
-
Morocco
-
Mozambique
-
Myanmar
-
Namibia
-
Nauru
-
Nepal
-
Netherlands
-
New Zealand
-
Nicaragua
-
Niger
-
Nigeria
-
Norway
-
Oman
-
Pakistan
-
Palau
-
Palestine
-
Panama
-
Papua New Guineaa
-
Paraguay
-
Peru
-
Philippines
-
Poland
-
Portugal
-
Qatar
-
Romania
-
Russia
-
Rwanda
-
Saint Kitts and Nevis
-
Saint Lucia
-
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
-
Samoa
-
San Marino
-
Sao Tome and Principe
-
Saudi Arabia
-
Senegal
-
Serbia
-
Seychelles
-
Sierra Leone
-
Singapore
-
Slovakia
-
Slovenia
-
Solomon Islands
-
Somalia
-
South Africa
-
South Korea
-
South Sudan
-
Spain
-
Sri Lanka
-
Sudan
-
Suriname
-
Sweden
-
Switzerland
-
Syria
-
Tajikistan
-
Tanzania
-
Thailand
-
Timor-Leste
-
Togo
-
Tonga
-
Trinidad and Tobago
-
Tunisia
-
Turkey
-
Turkmenistan
-
Tuvalu
-
Uganda
-
Ukraine
-
United Arab Emirates
-
United Kingdom
-
United States of America
-
Uruguay
-
Uzbekistan
-
Vanuatu
-
Venezuela
-
Vietnam
-
Yemen
-
Zambia
-
Zimbabwe
